Awe-Inspiring Examples Of Tips About What Is 40 KVA In KW
Understanding the Basics
1. What's the Deal with kVA and kW?
Alright, let's talk about power — not the kind that lets you bend spoons with your mind, but the electrical kind. You've probably seen terms like kVA and kW thrown around, especially when dealing with generators, UPS systems, or even large appliances. But what do they actually mean? More importantly, why should you care? Well, understanding the difference is crucial for properly sizing equipment and avoiding potential electrical nightmares. Think of it like this: you wouldn't want to put a tiny engine in a monster truck, right? Similarly, you wouldn't want an undersized generator trying to power your whole house during a blackout.
kVA stands for kilovolt-amperes, and it represents the apparent power. Think of it as the total power being supplied by an electrical source. It's like the total amount of beer in your glass, including the foam. kW, on the other hand, stands for kilowatts, and it represents the real power. This is the power that's actually doing the work, like running your appliances or lighting your home. It's the actual beer that you're drinking, minus the foam. The relationship between kVA and kW is defined by something called the power factor, which we'll get into later. But for now, just remember that kVA is the total power, and kW is the usable power.
So, why do we need both? Because electrical loads aren't always perfectly efficient. Some devices, especially those with motors or inductors (like refrigerators, air conditioners, and large machinery), draw what's called reactive power. This reactive power contributes to the kVA but doesn't actually do any work. It's essentially wasted energy circulating in the system. It's important because the equipment has to be built strong enough to handle the reactive power as well as the real power. Imagine a runner sprinting while carrying a backpack filled with rocks. The runner is working hard, but the rocks aren't helping. The kVA is the total effort, and the kW is the useful work.
Failing to understand these concepts can lead to some costly mistakes. Undersizing your generator, for instance, can cause it to overload and potentially damage your appliances. Oversizing, on the other hand, means you're paying for more capacity than you actually need, which is just a waste of money. Therefore, before you go buying any electrical equipment, it's worth taking the time to understand the kVA and kW ratings.

The Conversion
2. Crunching the Numbers
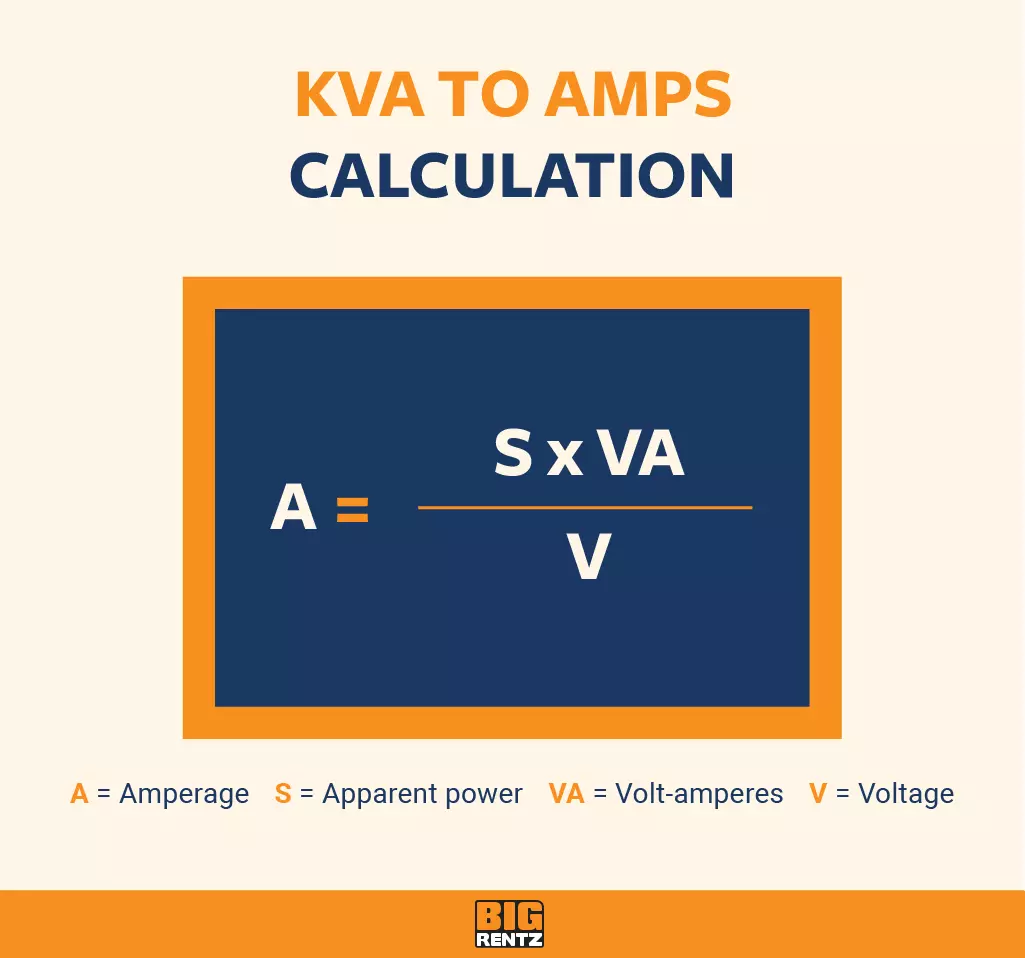
Okay, now that we've got the basics covered, let's get down to the main question: what is 40 kVA in kW? The answer, unfortunately, isn't a simple one-to-one conversion. To convert kVA to kW, you need to know the power factor. The power factor, as we mentioned earlier, is a measure of how efficiently electrical power is being used. It's a number between 0 and 1, with 1 being the most efficient. A power factor of 1 means that all the apparent power (kVA) is being used as real power (kW). In the real world, power factors are rarely perfect.
The formula for converting kVA to kW is pretty straightforward: kW = kVA x Power Factor. So, to figure out what 40 kVA is in kW, we need to know the power factor of the load. Let's say, for example, that the power factor is 0.8. This is a fairly common power factor for many industrial and commercial applications. Plugging the numbers into the formula, we get: kW = 40 kVA x 0.8 = 32 kW. Therefore, 40 kVA is equal to 32 kW at a power factor of 0.8.
But what if the power factor is different? Let's say it's 0.9. In that case, the calculation would be: kW = 40 kVA x 0.9 = 36 kW. So, 40 kVA is equal to 36 kW at a power factor of 0.9. As you can see, the power factor plays a significant role in determining the actual kW value. A higher power factor means more of the apparent power is being used as real power.
In many cases, you'll find the power factor listed on the equipment's nameplate. It's usually abbreviated as "PF" or "cos ". If you can't find the power factor, you can often assume a value of 0.8 for typical industrial and commercial loads. However, it's always best to check the equipment specifications to get an accurate value. Using an inaccurate power factor can lead to miscalculations and potential problems.

Power Factor
3. Digging Deeper
Let's spend a little more time on power factor, because its genuinely important — even if it sounds a bit dull. Imagine you're rowing a boat across a lake. The power factor is like how efficiently you're using your energy to move the boat forward. If you're rowing straight, all your effort is going into propelling the boat forward, and your power factor is high (close to 1). But if you're rowing at an angle, some of your energy is being wasted, and your power factor is lower.
A low power factor can cause several problems. Firstly, it means that you're using more kVA than you need to get the same amount of kW. This can overload your electrical system, causing voltage drops and equipment overheating. Secondly, utility companies often charge businesses extra for having a low power factor. This is because a low power factor increases the current flowing through the grid, which can lead to losses and inefficiencies. It's like the utility company is charging you extra for rowing your boat at an angle!
Fortunately, there are ways to improve your power factor. One common method is to use power factor correction capacitors. These capacitors supply reactive power to the system, reducing the amount of reactive power that needs to be drawn from the grid. This effectively "straightens out" your rowing stroke, making your electrical system more efficient. Power factor correction can save businesses money on their electricity bills and improve the overall performance of their electrical systems. Its like hiring a rowing coach for your electrical system.
To sum it up, power factor is not just some obscure technical term. It's a crucial factor in determining the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of your electrical system. By understanding power factor and taking steps to improve it, you can save money, reduce stress on your equipment, and even contribute to a more sustainable energy future. So, next time you see "PF" on a nameplate, don't ignore it!

Transformar Kva Em Kw FILECLOUD
Real-World Applications and Examples
4. Putting it All Together
Now that we've covered the theory, let's look at some practical applications of converting kVA to kW. One common scenario is sizing a generator for your home or business. If you know the total kW of the appliances and equipment you need to power, you can use the power factor to calculate the required kVA of the generator. For example, if you need to power 25 kW of equipment with a power factor of 0.8, you'll need a generator with a kVA rating of at least 31.25 kVA (25 kW / 0.8 = 31.25 kVA). Its wise to go a bit higher, just to be safe and have some headroom.
Another application is sizing an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) for critical equipment. A UPS provides backup power in the event of a power outage, ensuring that your sensitive electronics continue to operate. When sizing a UPS, it's important to consider both the kW and kVA requirements of the equipment you're protecting. Again, the power factor is key to making the right choice. You dont want your server crashing in the middle of the night just because you skimped on the UPS.
Commercial buildings also rely heavily on kVA to kW conversions. They often need to figure out the load on each circuit or the overall load for the building. Let's say a store is adding new freezers and needs to figure out if their existing electrical panel can handle the load. By knowing the kVA of the freezer, they can calculate the kW and determine if the circuit breaker has enough capacity. These calculations are crucial for ensuring safety and avoiding electrical overloads. Overloads are bad news they can cause fires and equipment damage.
Think about electric vehicle charging stations. As EV adoption grows, the demand for charging stations is increasing. When installing a charging station, the kVA and kW ratings are crucial for determining the size of the electrical service and the necessary wiring. Knowing the power factor helps electrical contractors make sure the new charging station does not overload the circuit. Its not just about plugging in a car, it is about proper electrical planning.

Genset ISUZU 40 KVA Silent STAMFORD WP44IJ Jual Jakarta
FAQ
5. Frequently Asked Questions about kVA and kW
Q: What happens if I ignore the power factor when sizing equipment?A: Ignoring the power factor can lead to undersizing your equipment, causing it to overload and potentially damage your appliances or generator. It can also lead to increased electricity bills if your utility company charges extra for low power factor.
Q: Is a higher power factor always better?A: Yes, a higher power factor (closer to 1) is generally better because it means that you're using electrical power more efficiently. This can lead to lower electricity bills, reduced stress on your equipment, and improved overall system performance.
Q: Can I improve the power factor of my home?A: While it's less common for homeowners to actively correct power factor, it's certainly possible. In most cases, the power factor of a typical home is good enough that there's no need for special equipment. However, if you have a lot of inductive loads (like motors or transformers) and you're concerned about energy efficiency, you can consult with an electrician about installing power factor correction capacitors.